A team of researchers is creating mobile robots for military applications that can determine, with or without human intervention, whether wheels or legs are more suitable to travel across terrains. The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) has partnered with Dr. Kiju Lee at Texas A&M University to enhance these robots' ability to self-sufficiently travel through urban military environments.
The DARPA OFFensive Swarm-Enabled Tactics (OFFSET) program awarded Lee, associate professor in the Department of Engineering Technology and Industrial Distribution and the J. Mike Walker '66 Department of Mechanical Engineering, and a team of graduate students another opportunity after her prior successful accomplishments on developing a mixed-reality swarm simulator with embedded consensus-based decision making for adaptive human-swarm teaming as part of the OFFSET Sprint-3. This project was showcased at OFFSET’s third field experiment (FX3) together with other participating teams.
“I have recently been awarded a new DARPA contract to join the OFFSET Sprint-5 effort focusing on enhancements to (the robot’s) physical testbeds,” Lee said. “Through this new project, I will develop unmanned ground vehicles with agile and versatile locomotive capabilities for urban military operations.”
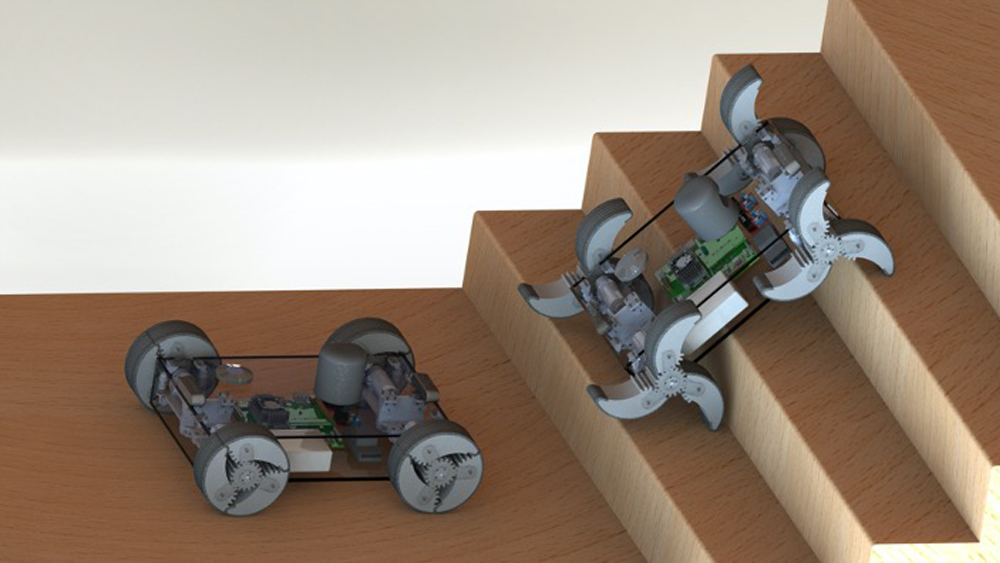
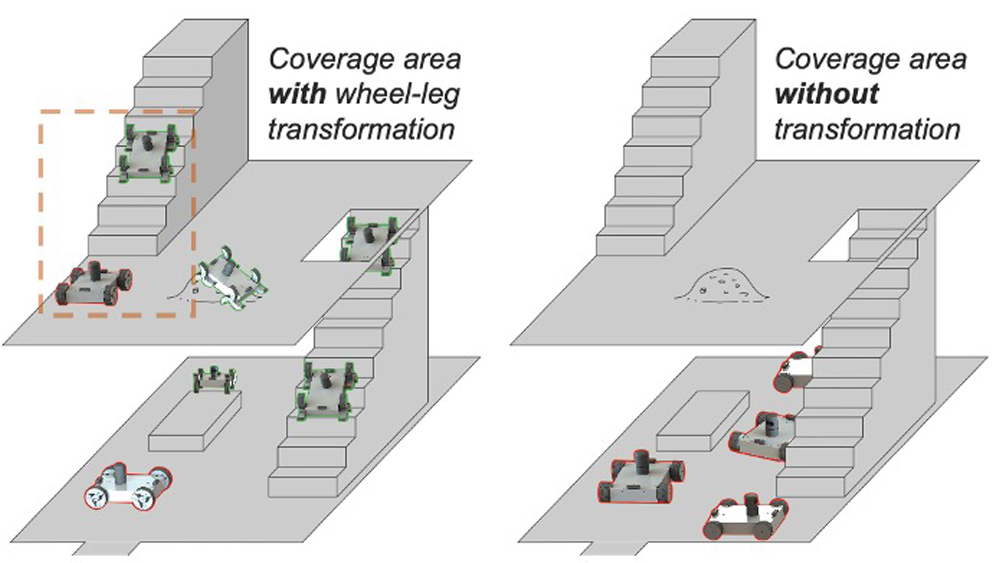
Lee and her team are developing an adaptable Wheel-and-Leg Transformable Robot (α-WaLTR) that can traverse over varying surfaces, including staircases, more efficiently. The α-WaLTR will move with wheels or legs depending on their immediate need and will be able to decide for itself which to use.

“Legged locomotion is more versatile, but suffers from inherent structural, mechanical and control complexities,” Lee said. “The proposed testbed will be equipped with novel wheel/leg transformable mechanisms, which can switch between the two locomotion modes actively adapting to its environment, but without needing any additional actuator.”
The team is rapidly developing prototypes and will showcase this new hardware platform at the OFFSET FX5 tentatively scheduled for February 2021.

Although created for military use, the team hopes this technology will transcend this field.
“While the current focus is on defense and other military applications, these types of adaptable mobile robots can be applied to many other areas, such as space, domestic service, surveillance and agriculture,” said Lee.
The OFFSET Sprint-5 effort is led by Lee along with the help of five graduate students and one undergraduate student — Chuanqi Zheng, Siddharth Sane, Vishnu Kalyanram, Kangneoung Lee, Sohil Parsana and Jenna Horn.